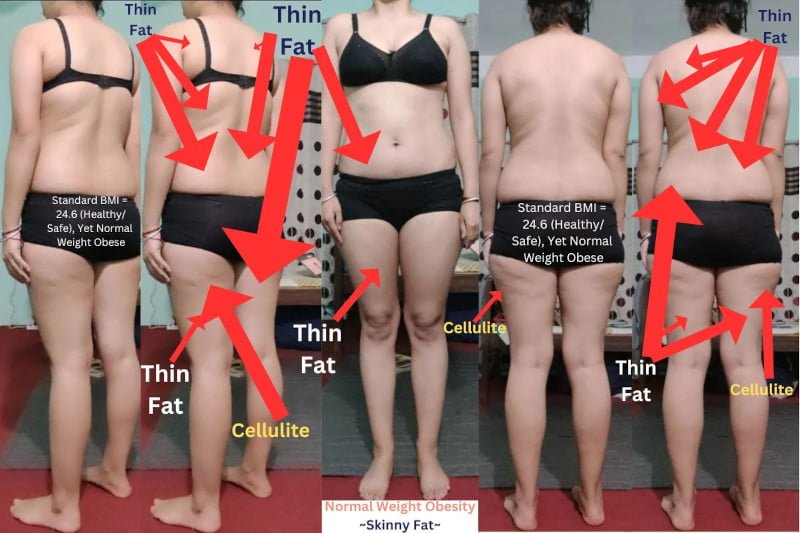
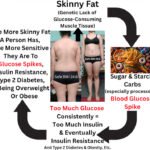
Skinny Fat & Insulin Resistance

If you are experiencing skinny fat then you are experiencing a lack of genetic muscle tissue (1, 2, 3, 4). Muscle tissue is a major glucose-sensitive tissue (5, 6, 7, 8) and directly affects the hormone insulin. What is the connection between skinny fat, insulin resistance, and excess regular white/yellow body fat (common adipose tissue) — IE being overweight or obese?
 Glucose is a type of sugar and the primary fuel (9, 10, 11)(calories) the human body uses to survive and function. Carbohydrates (12, 13) — including sugar and starch carbs — are the most common source of sugar. Refined sugar and starch carbs are particularly common in fast, junk, and processed foods.
Glucose is a type of sugar and the primary fuel (9, 10, 11)(calories) the human body uses to survive and function. Carbohydrates (12, 13) — including sugar and starch carbs — are the most common source of sugar. Refined sugar and starch carbs are particularly common in fast, junk, and processed foods.
Fiber carbs, vital (14, 15, 16, 13) for proper digestion and health, contain no sugar and cannot be broken down into sugar. Fiber is typically deficient (15, 17, 18, 19) in fast, junk, and processed foods — IE ultra-processed foods (UPFs) — which make up roughly 60% of the average American diet. Low carb means low sugar and starch carbs.
Skinny Fat & Insulin Resistance

When consumed, sugar and starch carbs are readily broken down by the body into glucose (fuel/calories). To process increased blood glucose (sugar) levels, the pancreas releases insulin to regulate blood glucose. The more glucose, the more insulin that is required. Sugar and starch carbs — especially when refined, which is very common in fast, junk, and processed foods — cause a significant increase, AKA a glucose spike, that stresses the body’s insulin response even more.

Over time, the body becomes less sensitive to insulin, eventually becoming insulin-resistant. The pancreas cannot produce the amount of insulin needed to regulate blood glucose. The excess glucose is stored as glycogen (20, 21) in the muscles, liver, etc. Any further excess is stored as regular white/yellow body fat (common adipose tissue)(21, 22, 9, 10, 11, 20). All of this leads to type 2 diabetes and being overweight and obese, at least.
Muscle tissue consumes a significant amount of glucose for maintenance and functioning. The more genetic default muscle tissue a person naturally, genetically has, the stronger their metabolism (23) and the more glucose they consume. If you are experiencing skinny fat, you have less muscle tissue, and thus, your body naturally burns less glucose.
How Do I Know If I Am Skinny Fat?
 The Free Scientific Skinny Fat Test will give you a sense of whether you are experiencing skinny fat. As will the Free Scientific Skinny Fat Quiz. But to really know if you are experiencing skinny fat, take the Official Scientific Body Type Quiz.
The Free Scientific Skinny Fat Test will give you a sense of whether you are experiencing skinny fat. As will the Free Scientific Skinny Fat Quiz. But to really know if you are experiencing skinny fat, take the Official Scientific Body Type Quiz.
Our MRI Study (24) will give medical doctors the first-ever official way to diagnose skinny fat and prove once and for all what skinny fat is.
Once you know whether or not you are experiencing skinny fat where genetically you should have default genetic muscle tissue, you can better understand your metabolism (23) and how sensitive your body is to excess glucose and insulin resistance. The more skinny fat you are experiencing, the more sensitive you are to glucose spikes and insulin resistance.
What Can I Do About Skinny Fat & Insulin Resistance
 Adding muscle mass (25, 26, 27) is the best way to reduce skinny fat. The more muscle mass you safely add, along with proper diet, exercise, and lifestyle, the more you mitigate insulin resistance. The more you mitigate insulin resistance, the more regular white/yellow body fat you can safely lose. And the easier all that is to manage in the short and long term.
Adding muscle mass (25, 26, 27) is the best way to reduce skinny fat. The more muscle mass you safely add, along with proper diet, exercise, and lifestyle, the more you mitigate insulin resistance. The more you mitigate insulin resistance, the more regular white/yellow body fat you can safely lose. And the easier all that is to manage in the short and long term.
The key to successful, sustainable regular fat weight loss, reversing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, fixing skinny fat, and returning to a state of health is understanding your unique genetic body composition — including any skinny fat — relative to choosing and eating a healthy diet (13); specifically in terms of sugar and starch carbs (low-carb diet). And then properly implementing healthy exercise (27, 28, 25, 24) and lifestyle (29) (sleep, stress, environment) routines.
Male, Skinny Fat But Muscular – Skinny Fat Question
References
- Skinny Fat Science: What Is Skinny Fat?, July 2, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/what-is-skinny-fat/
- Skinny Fat Science: Skinny Fat Is More Than Just Normal-Weight Obesity, April 2, 2025. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/skinny-fat-is-more-than-just-normal-weight-obesity/
- Skinny Fat Science: Is Skinny Fat Genetic?, November 27, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/is-skinny-fat-genetic/
- Skinny Fat Science: Is Muscle/Mass Genetic and How Does It Affect Skinny Fat?, November 20, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/is-muscle-mass-genetic-and-how-does-it-affect-skinny-fat/
- American Diabetes Association: Assessment of Tissue-Specific Glucose Uptake: Teaching an Old 2-DOG New Tricks, March 1, 2024, Max C. Petersen and Michael J. Jurczak. https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/73/3/355/154224/Assessment-of-Tissue-Specific-Glucose-Uptake
- NIH, National Library of Medicine: Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake, April 26, 2021, Karla E Merz and Debbie C Thurmond. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8074531/
- ScienceDirect, Cell Metabolism: The many actions of insulin in skeletal muscle, the paramount tissue determining glycemia, April 6, 2021, Volume 33, Issue 4, Pages 758-780, Lykke Sylow, Victoria, Tokarz, Erik A. Richter, and Amira Klip. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413121001273
- European Society of Endocrinology: Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue and liver: a positron emission tomography study, May 2018, Volume 178, Issue 5, Pages 523–531, Miikka-Juhani Honka, Aino Latva-Rasku, Marco Bucci, Kirsi A Virtanen, Jarna C Hannukainen, Kari K Kalliokoski, and Pirjo Nuutila. https://academic.oup.com/ejendo/article/178/5/523/6655377
- NIH, National Library of Medicine: Physiology, Glucose Metabolism, July 17, 2023, Mihir N. Nakrani, Robert H. Wineland, and Fatima Anjum. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560599/
- WebMD: What is Glucose?, April 2, 2024, Stephanie Watson and Stephanie Booth (Medically reviewed by Zilpah Sheikh, MD). https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/glucose-diabetes
- Wikipedia: Glucose. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose
- MedlinePlus: Carbohydrates. https://medlineplus.gov/carbohydrates.html
- Skinny Fat Science: The Best Skinny Fat Diet, According to Science, July 29, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/the-best-skinny-fat-diet-according-to-science/
- Cleveland Clinic: Why Is Fiber So Important?, https://health.clevelandclinic.org/fiber
- Mayo Clinic, Nutrition and healthy eating: Dietary fiber: Essential for a healthy diet, December 11, 2014, Mayo Clinic Staff. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fiber/art-20043983
- Harvard Health Publishing: The facts on fiber, November 1, 2024, Matthew Solan (Executive Editor for Harvard Men’s Health Watch)(Reviewed by Howard E. LeWine, MD, Chief Medical Editor). https://www.health.harvard.edu/nutrition/the-facts-on-fiber
- NIH, National Library of Medicine: Closing America’s Fiber Intake Gap, July 7, 2016, Diane Quagliani and Patricia Felt-Gunderson. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6124841/
- American Society for Nutrition: Most Americans are not getting enough fiber in our diets, June 9, 2021, ASN Staff. https://nutrition.org/most-americans-are-not-getting-enough-fiber-in-our-diets/
- Eating Well: 6 Sneaky Signs You’re Not Eating Enough Fiber, According to a Dietitian, June 11, 2021, Ayat Sleymann, M.S., RDN. (Reviewed by Dietitian Victoria Seaver, M.S., RD). https://www.eatingwell.com/article/7907005/sneaky-signs-youre-not-eating-enough-fiber-according-to-a-dietitian/
- NIH, National Library of Medicine: Stranger in a Strange Land: Roles of Glycogen Turnover in Adipose Tissue Metabolism, April 29, 2011, Kathleen R. Markan, Michael J. Jurczak, and Matthew J. Brady. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2826604/
- University of Utah Health: How Sugar Converts to Fat, September 1, 2023, Dr. Juan Gallegos, liver expert at the University of Utah Hospital. https://healthcare.utah.edu/the-scope/health-library/all/2018/08/how-sugar-converts-fat
- Skinny Fat Science: Are Regular Fat and Skinny Fat the Same Thing?, August 28, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/are-regular-fat-and-skinny-fat-the-same-thing/
- Skinny Fat Science: How Skinny Fat Affects Metabolism, August 7, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/how-skinny-fat-affects-metabolism/
- Skinny Fat Science: Scientific Skinny Fat MRI Study – Proving What Skinny Fat Is, March 26, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/scientific-skinny-fat-mri-study-proving-what-skinny-fat-is/
- Skinny Fat Science: Best Skinny Fat Resistance Exercises, September 4, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/best-skinny-fat-resistance-exercises/
- Skinny Fat Science: Resistance Training for Skinny Fat – Weight Lifting, 40 Optimal Exercises (with Images), May 7, 2025. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/resistance-training-for-skinny-fat-weight-lifting-40-optimal-exercises-with-images/
- Skinny Fat Science: The Best Skinny Fat Exercise, According to Science, August 2, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/the-best-skinny-fat-exercise-according-to-science/
- Skinny Fat Science: Best Skinny Fat Cardio Exercises, September 11, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/best-skinny-fat-cardio-exercises/
- Skinny Fat Science: The Best Skinny Fat Lifestyle, According to Science, August 14, 2024. https://skinnyfat.fellowone.com/skinny-fat-science/the-best-skinny-fat-lifestyle-according-to-science/